Leading Network Outsourcing Companies to Enhance Efficiency

Comprehensive Guide to Network Outsourcing: Managed Network Services, Benefits, and Solutions
Network outsourcing has emerged as a pivotal strategy for businesses seeking to enhance operational efficiency and focus on core competencies. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of network outsourcing, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and the various solutions available. Readers will gain insights into how managed network services can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve security. As organizations grapple with the complexities of modern IT infrastructure, network outsourcing offers a viable solution to address these challenges. This article will cover the definition of network outsourcing, its key benefits, common services that are outsourced, potential challenges, leading providers, and emerging trends shaping the future of network management.
Industry Insights and Market Overview
The landscape of network outsourcing is rapidly expanding, driven by the increasing complexity of IT environments and the strategic imperative for businesses to focus on core competencies. Recent market analyses indicate that the global managed network services market is projected to reach significant valuations, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 11.5% over the next five years. This robust growth is fueled by several critical factors, including the accelerating pace of digital transformation, the escalating threat of sophisticated cyberattacks, and the continuous pressure on organizations to optimize operational costs while maintaining high performance.
Leading industry reports consistently highlight that businesses leveraging network outsourcing often report substantial improvements in network uptime, a strengthened security posture, and overall IT efficiency. This strategic shift is not merely a cost-cutting measure but a fundamental re-evaluation of how critical network infrastructure is managed to support innovation and business resilience in an increasingly interconnected and competitive world.
What is Network Outsourcing and How Does It Work?
Network outsourcing refers to the practice of delegating the management of network infrastructure and services to third-party providers. This approach allows businesses to leverage specialized expertise while focusing on their core operations. By outsourcing network management, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce overhead costs. The core concept revolves around the collaboration between the business and managed service providers (MSPs) to ensure seamless network performance and reliability.
Defining Network Outsourcing and Its Core Concepts
At its essence, network outsourcing involves entrusting specific IT functions to external vendors. This can include tasks such as network monitoring, maintenance, and support. The primary goal is to optimize network performance while minimizing the burden on internal resources. Key components of network outsourcing include service level agreements (SLAs), which define the expected performance and responsibilities of both parties, and the use of advanced technologies to facilitate efficient service delivery.
Understanding Managed Network Services and Network as a Service
Managed network services (MNS) encompass a range of IT functions provided by third-party vendors, including network monitoring, security, and data management. In contrast, Network as a Service (NaaS) offers a more flexible approach, allowing businesses to access network resources on-demand. This model enables organizations to scale their network capabilities according to their needs, providing a cost-effective solution for managing fluctuating workloads. Both MNS and NaaS play crucial roles in enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring robust network performance.
What Are the Key Benefits of Outsourced Network Management?

Outsourcing network management presents several advantages that can significantly impact a business’s operational efficiency and bottom line. By leveraging external expertise, organizations can achieve cost savings, access advanced technologies, and enhance their overall security posture.
- Cost Savings: Outsourcing network management can lead to substantial cost reductions by eliminating the need for in-house IT staff and infrastructure investments. Businesses can redirect these savings towards core activities that drive growth, with many reporting up to 30% reduction in operational IT costs.
- Access to Expertise: Managed service providers bring specialized knowledge and experience, ensuring that businesses benefit from the latest technologies and best practices in network management, often exceeding the capabilities of internal teams.
- Enhanced Security: Outsourcing network management allows organizations to leverage the security expertise of MSPs, who implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations, significantly reducing the risk of breaches.
How Does Network Outsourcing Deliver Cost Savings and Efficiency?
Network outsourcing can deliver significant cost savings through various mechanisms. By eliminating the need for in-house IT staff, businesses can reduce payroll expenses and associated overhead costs. Additionally, outsourcing allows organizations to access advanced technologies without the burden of large capital expenditures. For instance, many MSPs offer subscription-based pricing models, enabling businesses to pay only for the services they use, further enhancing cost efficiency and predictability. This model has been proven to optimize resource allocation and improve overall operational agility.
In What Ways Does Outsourcing Enhance Network Security and Compliance?
Outsourcing network management enhances security by providing access to specialized expertise and advanced security technologies. Managed service providers implement comprehensive security measures, including next-generation firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security audits. This proactive approach helps organizations mitigate risks and ensure compliance with stringent industry regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Furthermore, MSPs stay updated on the latest security threats and vulnerabilities, allowing them to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging challenges, a critical capability for modern businesses.
Which Network Infrastructure Management Services Are Commonly Outsourced?
Businesses often outsource various network infrastructure management services to enhance efficiency and focus on core operations. Commonly outsourced services include network monitoring, data backup, and cybersecurity management, all delivered with a high degree of specialization.
Exploring Managed LAN, WAN, and Cloud Network Solutions
Managed Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) solutions are frequently outsourced to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These services encompass the management of network devices, traffic optimization, and proactive troubleshooting. Additionally, cloud network solutions provide businesses with scalable resources, enabling them to adapt to changing demands without significant upfront investments, thereby fostering greater agility and innovation.
How Do Managed Service Providers Support Scalability and Flexibility?
Managed service providers play a crucial role in supporting scalability and flexibility within organizations. By offering on-demand resources and services, MSPs enable businesses to quickly adjust their network capabilities in response to changing market conditions and technological advancements. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for companies experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand, allowing them to maintain operational efficiency without overcommitting resources or incurring unnecessary capital expenditures.
What Are the Challenges and Considerations in Network Outsourcing?
While network outsourcing offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that organizations must consider. Key concerns include security, control, and vendor lock-in, which require careful strategic planning and due diligence.
Addressing Security, Control, and Vendor Lock-in Concerns
Security remains a primary concern for businesses considering network outsourcing. Organizations must ensure that their chosen managed service provider implements robust security measures to protect sensitive data, adhering to the highest industry standards. Additionally, businesses should maintain a clear level of control over their network infrastructure to avoid potential issues related to vendor lock-in. This can be achieved by negotiating favorable contract terms, ensuring data ownership remains with the organization, and establishing clear exit strategies from the outset.
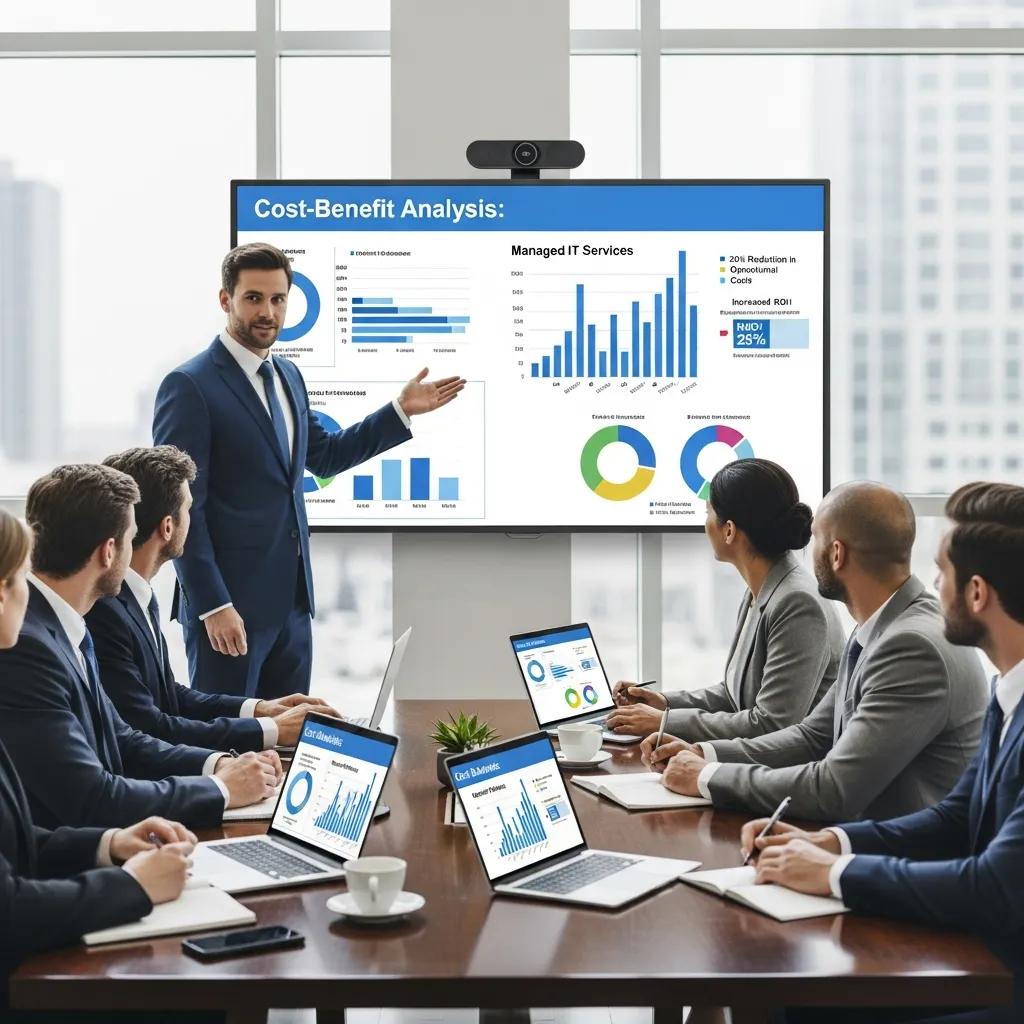
How to Evaluate Costs and Return on Investment for Outsourcing
Evaluating the costs and return on investment (ROI) for network outsourcing requires a comprehensive analysis of both direct and indirect expenses. Organizations should consider factors such as the total cost of ownership, potential savings from reduced in-house staffing, and the quantifiable value of enhanced security, improved efficiency, and access to cutting-edge technology. By conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and projecting long-term gains, businesses can make informed, strategic decisions about whether outsourcing is the right strategy for their network management needs.
Who Are the Leading Network Outsourcing Providers and How to Choose One?
Selecting the right network outsourcing provider is critical to achieving desired outcomes and maximizing the benefits of this strategic approach. Businesses should consider various factors when evaluating potential partners to ensure a successful long-term collaboration.
Top Managed Service Providers and Their Service Offerings
Several leading managed service providers offer a comprehensive range of network outsourcing solutions, distinguished by their global reach, technological prowess, and specialized expertise. These providers typically offer services such as advanced network monitoring, robust cybersecurity frameworks, and sophisticated data management solutions. When evaluating potential partners, organizations should assess their proven track record, depth of expertise, breadth of service offerings, and customer reviews to ensure alignment with their specific operational and strategic needs.
What Criteria Should Businesses Use to Select a Network Outsourcing Partner?
When choosing a network outsourcing partner, businesses should consider critical criteria such as extensive industry experience, clearly defined and enforceable service level agreements (SLAs), and exceptional customer support. Additionally, organizations should evaluate the provider’s ability to scale services seamlessly according to their evolving needs, their commitment to maintaining robust security measures, and their adherence to relevant compliance standards. By establishing clear and comprehensive selection criteria, businesses can identify the most suitable and authoritative partner for their network management requirements, ensuring a secure and efficient future.
What Are the Emerging Trends and Future Outlook for Network Outsourcing in 2025?

As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, network outsourcing is expected to undergo significant and transformative changes. Emerging trends include the deeper integration of artificial intelligence, advanced cloud computing paradigms, and sophisticated automation into network management practices, redefining efficiency and capability.
How Are AI, Cloud Computing, and Automation Shaping Network Outsourcing?
Artificial intelligence and automation are fundamentally transforming network management by enabling more efficient monitoring, predictive analytics, and rapid response to network issues. These cutting-edge technologies allow managed service providers to proactively identify and address potential problems before they impact business operations, significantly reducing downtime and improving performance. Additionally, cloud computing facilitates greater flexibility, scalability, and resilience, allowing organizations to adapt their network resources dynamically to meet changing demands and support innovative business models.
What Role Do Strategic Partnerships and Hybrid Models Play in Future Network Management?
Strategic partnerships and hybrid models are becoming increasingly important in the complex landscape of modern network management. By collaborating with multiple service providers, organizations can leverage a diverse range of specialized expertise and advanced technologies, creating a robust and resilient network ecosystem. This approach enables businesses to create customized solutions that align precisely with their specific needs while maintaining unparalleled flexibility and agility in their network management strategies, positioning them for future growth and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should businesses consider when transitioning to network outsourcing?
When transitioning to network outsourcing, businesses should evaluate several key factors. First, a thorough assessment of your organization’s specific needs, including the types of services required and the level of expertise needed, is paramount. It’s also crucial to consider the potential impact on existing staff and operations, ensuring a smooth internal transition. Additionally, businesses must rigorously review the security measures of potential providers, ensuring they align with or exceed industry standards and regulatory requirements. Finally, a deep understanding of the terms of service level agreements (SLAs) and the provider’s proven track record can help ensure a seamless transition and robust ongoing support.
How can businesses ensure data security when outsourcing network management?
To ensure data security when outsourcing network management, businesses should conduct thorough due diligence on potential managed service providers (MSPs). This includes reviewing their security protocols, compliance with international and industry-specific regulations, and their history of data breach prevention and response. Organizations should also negotiate contracts that include specific, enforceable security measures, such as advanced encryption, regular third-party audits, and clear incident response plans. Implementing a clear data ownership policy and maintaining open, transparent communication with the provider about security practices can further enhance data protection and significantly mitigate risks associated with outsourcing.
What are the potential risks of vendor lock-in in network outsourcing?
Vendor lock-in occurs when a business becomes overly dependent on a specific service provider, making it difficult and costly to switch vendors or bring services back in-house. This can lead to increased costs, reduced flexibility, and diminished bargaining power. To mitigate this critical risk, organizations should negotiate favorable contract terms that allow for easy exit strategies, ensure data portability, and define clear intellectual property rights. Additionally, diversifying service providers and maintaining a foundational level of in-house expertise can help businesses avoid becoming too reliant on a single vendor, thus preserving their operational agility and strategic independence.
How can businesses measure the success of their network outsourcing strategy?
Measuring the success of a network outsourcing strategy involves tracking several key performance indicators (KPIs) and strategic objectives. Businesses should rigorously evaluate cost savings against projections, service uptime and availability, and response times to incidents, comparing them to pre-outsourcing benchmarks. Additionally, assessing user satisfaction, the overall impact on operational efficiency, and the ability to innovate can provide invaluable insights into the effectiveness of the outsourcing arrangement. Regular performance reviews and structured feedback sessions with the managed service provider are essential to identify areas for continuous improvement and ensure that the partnership consistently meets the organization’s evolving needs and strategic goals.
What emerging technologies should businesses watch for in network outsourcing?
Businesses should keep a vigilant eye on several emerging technologies that are profoundly shaping the future of network outsourcing. Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being leveraged for predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated network management, significantly enhancing efficiency and response times. Additionally, advancements in edge computing and 5G connectivity are enabling more flexible, distributed, and high-performance network solutions. Automation tools, particularly Robotic Process Automation (RPA), are also becoming essential for streamlining routine operations and drastically reducing human error. Staying informed about these transformative technologies can help organizations leverage new opportunities and maintain a competitive edge in their network management strategies.
How do regulatory compliance requirements affect network outsourcing decisions?
Regulatory compliance requirements significantly influence network outsourcing decisions, as businesses must ensure that their managed service providers adhere to all relevant local, national, and international laws and industry standards. This includes stringent data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and industry-specific mandates, which dictate strict security measures for handling sensitive information. Organizations must thoroughly assess the compliance track record and certifications of potential providers and ensure that their services align perfectly with all applicable regulatory frameworks. Failure to comply can result in severe legal penalties, substantial financial fines, and irreparable damage to reputation, making it absolutely essential to prioritize compliance as a non-negotiable factor in the outsourcing selection process.